|
The 65th European Study Group with Industry 2008
Problems
|
|
|
|
Warehouse
storing and collecting of parts
(problem
proposed by GROHE)
|
|
|
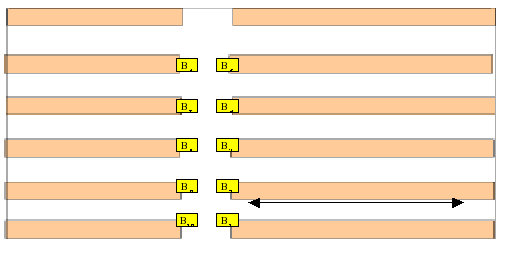
The
purpose of this problem is to optimize the time taken by fork-lifts
to collect and store parts in a warehouse.
The layout of the warehouse is shown in the figure. There
are three fork-lifts collecting parts from the shelves and taking
them to a fixed base point, per each corridor, denoted by Bi.
At the same time, they take parts from B and store them in the
shelves. At each point in time, a given fork-lift may carry only one
type of parts which is to be either stored or collected. The storage
place of a given part is predetermined. Denoting
the parts to be collected and stored by C1,...,Cm and
S1,...,Sm,
respectively, we want to produce a list with the optimal pairing of
Ci's
to Sj's
(leaving |m-n| items unpaired if necessary) which minimizes the total
storage-collection time. Possible
further questions include the optimization of the layout of the
shelves, and also of the organization of the storage of parts
depending on past history.
|
|
|
|
|
Electrostatic
separation of rubber and textiles
(problem proposed by Biosafe)
|
|
In
the process of recycling rubber from tires, the end product should be
as clear of foreign particles as possible. Of all the tire
components, textiles prove to be the hardest to remove by the methods
already being employed by Biosafe (vibration, magnetostatic, etc).
Although for the larger grains the present process is satisfactory,
for smaller particles (typically under 2mm) it is difficult to
separate the textiles from the rubber. Because of this, the company
is thinking of using electrostatic plates as a mean to eliminate the
textiles in the final stage. However, existing methods of this type
do not necessarily extend to the materials being used, and they would
want to know if the method would prove to be feasible, efficient and
safe.
|
|
Cooling
of a rotor
(problem proposed by Biosafe)
|
|
A
steel rotor which is used to shred tires for recycling functions at
450 r.p.m. and has an allowable working temperature range. It is not
known what the optimal temperature is, but it should not exceed 80oC.
Very low temperatures, on the other hand, are not efficient –
typically, the first half hour has a lower output than the stationary
regime. In
the present configurations, the temperature can easily become higher
than what is acceptable (at least 100oC-150oC),
and the company is considering the possibility of cooling the system
by circulating a liquid (possibly water) inside the rotor. The
company would like to know how the cooling should be made, and if it
will be safe and efficient to have the cooling liquid inside the
drum.
|
|
|
|
|
Optimization
of task assignment in a factory
(problem proposed by For Ever)
|
|
In
order to carry out their orders of shoe soles, this company has a
number of tasks T1,...,Tn
of different lengths to be assigned to groups of machines. Each group
is operated by one worker (two in one case), and an operation cycle
corresponds to injection, cooling, and removal of the sole. The time
taken at each step varies from one order to another, and when
starting a new order a machine needs to be tuned, which takes some
extra time. Machines are working in parallel. At the moment the
assignment is carried out empirically, and the problem proposed is to
optimize the procedure.
|
|
|